East Central Europe (4,365 – 2,638 …
Years: 4365BCE - 2638BCE
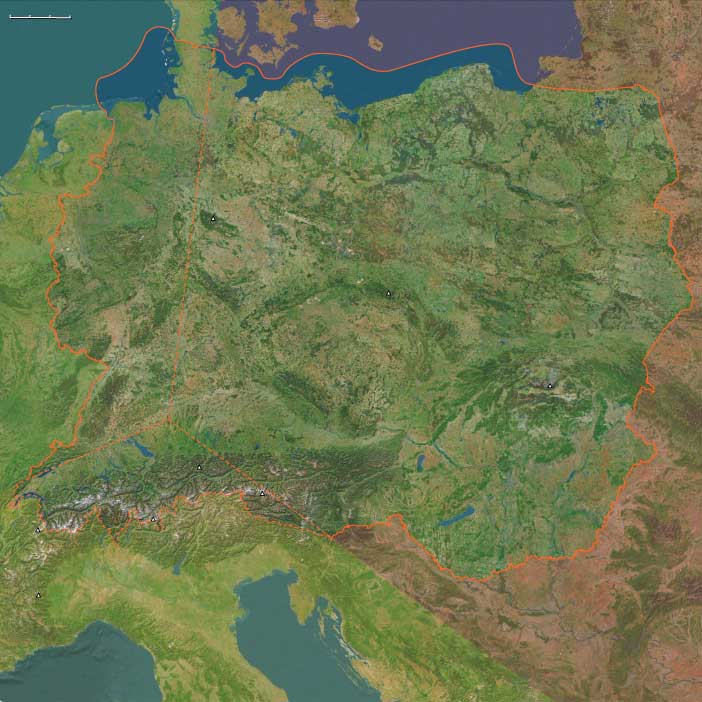
East Central Europe (4,365 – 2,638 BCE) Late Neolithic/Chalcolithic — Megasites, Copper, and Corded Ware
Geographic and Environmental Context
East Central Europe includes Turkey-in-Europe (Thrace); Greece’s Thrace; Bulgaria (except its southwest); Romania & Moldova; northeastern Serbia; northeastern Croatia; extreme northeastern Bosnia & Herzegovina.
-
Anchors: Lengyel–Tisza cultures in Carpathian Basin, Bohemia–Poland Funnelbeaker (TRB), Corded Ware expansions (c. 2900–2300 BCE).
Climate & Environmental Shifts
-
Stable but trending cooler; loess soils productive; river valleys sustained denser populations.
Subsistence & Settlement
-
Farming diversified; copper metallurgy introduced; cattle herding intensified.
-
Large villages and proto-towns in Tisza–Danube basin.
-
Corded Ware horizon added mobile herders with cattle/horses.
Technology & Material Culture
-
Painted ceramics (Lengyel, Tisza); copper ornaments/tools.
-
Corded Ware pottery, battle-axes.
Movement & Interaction Corridors
-
Amber routes (Baltic to Carpathian Basin); Danube–Elbe corridors.
-
Steppe contacts brought horse and wagon innovations.
Cultural & Symbolic Expressions
-
Ritual figurines, painted pottery; burial rites diversified (flat graves, kurgan intrusions).
Groups
- Lengyel culture
- Rössen Culture
- Funnelbeaker Culture
- Corded Ware culture
- Bell-Beaker, or beaker, culture
Topics
- Neolithic Europe
- Chalcolithic Epoch, or Copper Ages
- Older Peron Transgression during the Neolithic Subpluvial
- Younger Peron Transgression during the Neolithic Subpluvial
- 5.9 kiloyear event during the Neolithic Subpluvial
- Subboreal Period during the Neolithic Subpluvial
- Piora Oscillation ending the Neolithic Subpluvial
- Subboreal Period