The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami …
Years: 405BCE - 394BCE
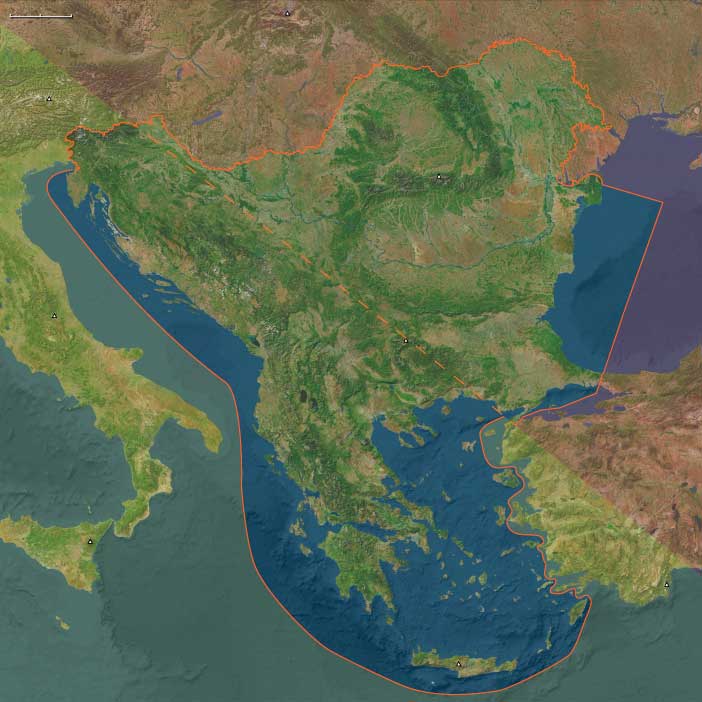
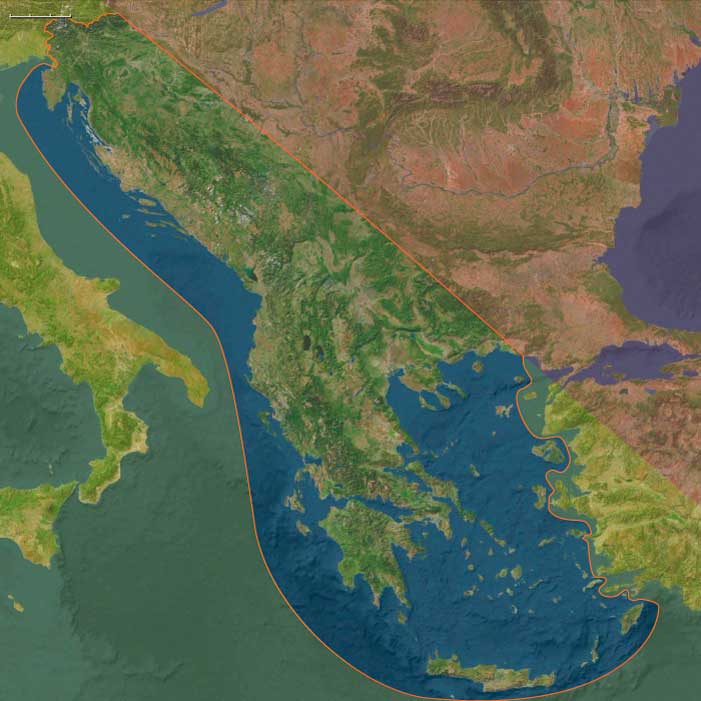
The destruction of Athens' fleet at Aegospotami effectively ends the Peloponnesian War, and Athens surrenders in the following year.
Sparta has resoundingly failed to destroy the Athenian empire, and in this sense Athens, whatever its financial and human losses, has won the Peloponnesian War.
Thucydides observes that contemporary Greeks were shocked not that Athens eventually fell after the defeat in Sicily, but rather that it fought on for as long as it did, so devastating were the losses suffered.
The Corinthian War, pitting Sparta against a coalition of four allied states, Thebes, Athens, Corinth, and Argos, which are initially backed by Persia, lasts from 395 BCE until 387 BCE.
The immediate cause of the war was a local conflict in northwest Greece in which both Thebes and Sparta intervened.
The results are inconclusive: under the Peace of Antalcidas, dictated by Persia, Ionia is ceded to Persia and the Boeotian league is dissolved, as is the union of Argos and Corinth.
People
Groups
- Thebes, City-State of
- Argos, City-State of
- Sicily, classical
- Carthage, Kingdom of
- Corinth, City-State of
- Segesta, (Elymian-Ionian Greek) city-state of
- Magna Graecia
- Syracuse, Corinthian city-state of
- Croton (Achaean Greek) city-state of
- Gela (Dorian Greek) city-state of
- Selinus, (Dorian Greek) city-state of
- Etruria
- Camerina (Dorian Greek) city-state of
- Akragas (Dorian Greek) city-state of
- Boeotian League
- Roman Republic
- Athenian Empire (Delian League)
- La Tène culture
Topics
- Iron Age Europe
- Iron Age Cold Epoch
- Classical antiquity
- Iron Age China
- Roman-Etruscan Wars, Early
- Pre-Roman Iron Age of Northern Europe
- Sicilian Wars, or Carthaginian-Syracusan Wars
- Peloponnesian War, Second or Great
- Decelean War, or Ionian War
- Sicilian War, Second, or Second Carthaginian-Syracusan War
- Himilco's War
- Roman War with Veii, Second
- Ten Thousand, March of the
- Corinthian War
Commodoties
Subjects
- Commerce
- Watercraft
- Environment
- Labor and Service
- Decorative arts
- Conflict
- Faith
- Government
- Custom and Law
- Technology
- Archaeology